S tructure
Alkenes
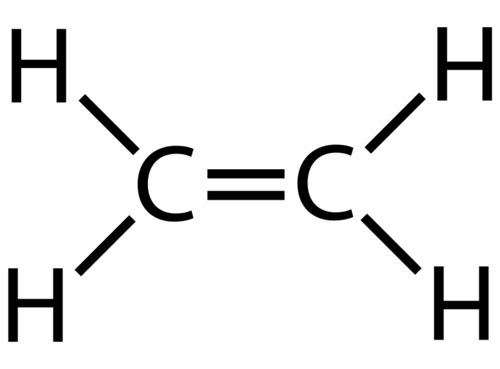
Alkenes are organic compounds that have double bonds/one sigma and one pie bond connected to the main/parent carbon chain. These structures are represented using digrams/structure drawings that have two lines connecting carbon atoms instead of one. Due to the nature of the extra bond, the atom changes properties and identity due to where the side chains/atoms coming off of the double bonded atoms are located. This is called a cis/trans alkene structure.
General Formula
The general formula for alkenes (or cycloalkanes):
CnH2n
where n is all real numbers that are positive.

B ack
Alkynes

Alkynes are similar to Alkenes, except that they have triple bonds (or one sigma and two pi) in the main chain. Unlike alkanes, they do not exhibit cis/trans structures due to the limit on how many atoms can be bonded to the triple bond atoms (one to each), and are represented using three lines when drawing their structure.
General Formula
The general formula for alkynes:
CnH2n-2
where n is all real numbers that are positive.