S tructure
Benzene
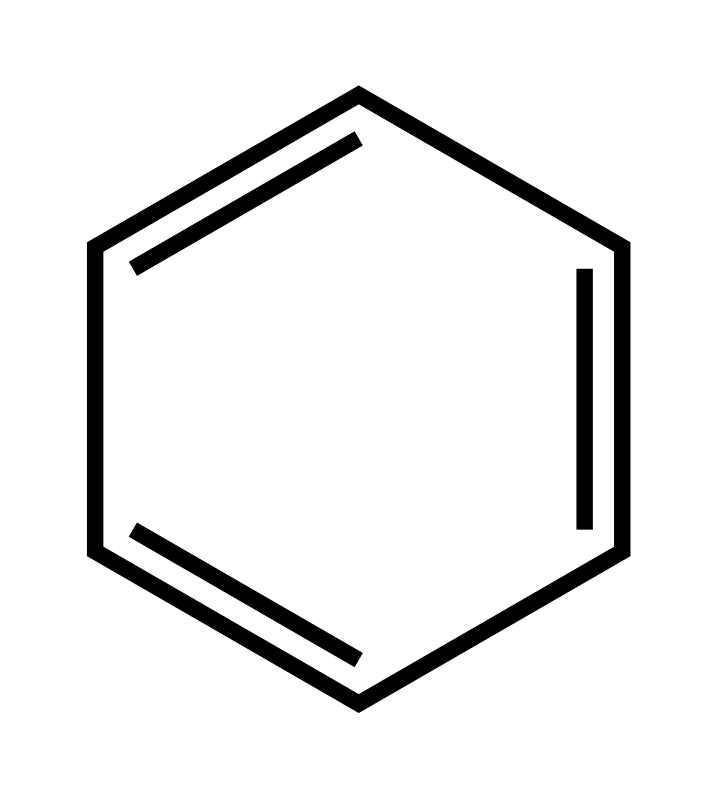
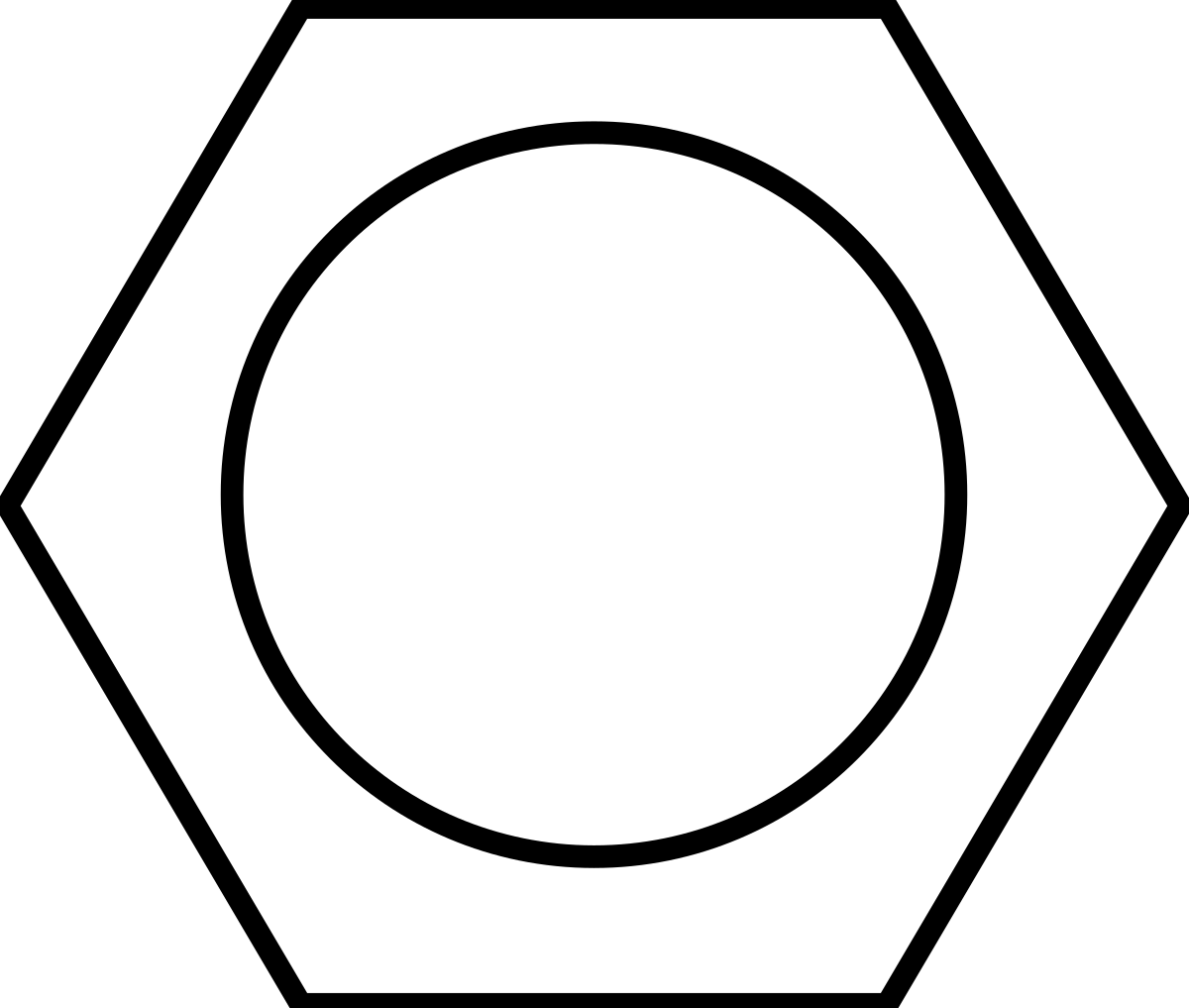
Benzene is represented as a six carbon ring that has three double bonds in its cyclic structure. These three pi bonds are able to move from each carbon bond to the next freely, resulting in delocalized electrons, these delocalized electrons result in the compound being incredibly stable. This means that while the compound has three pi bonds, it is considered/acts like its saturated. This delocalization can be represented as a circle in the drawing of benzene, such as the structure below (which is due to how the delocalized electrons in the p sub orbitals orient themselves):
General Formula
The general formula for aromatics (benzene):
CnHn
where n is all real numbers that are positive.

B ack